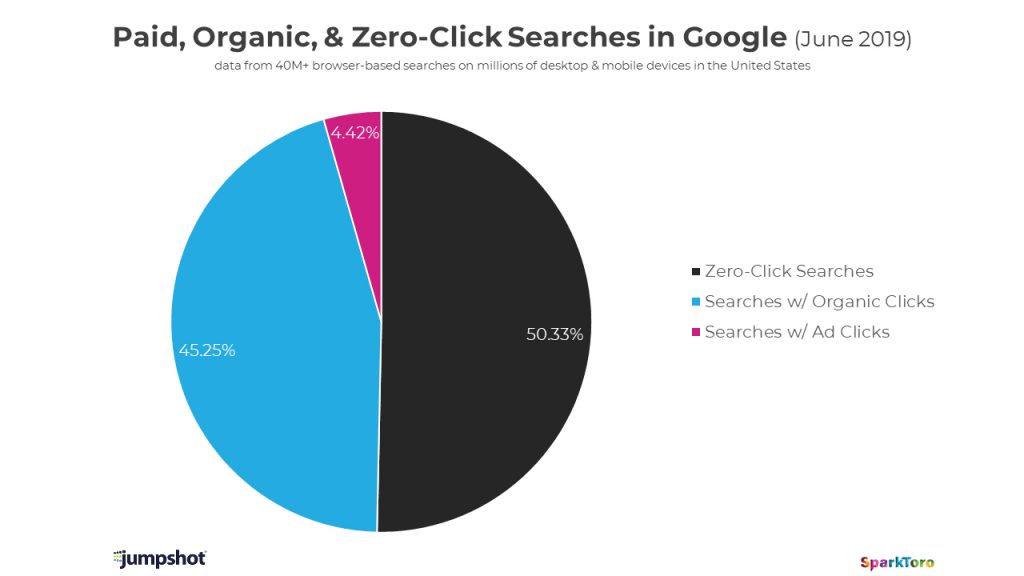
Less than half of Google searches now result in a click
Some mixed news about Google for publishers and advertisers in the past few weeks. We’ll start with the not-so-good news about clicks, especially as it turns out, for mobile, detailed by Rand Fishkin…
We’ve passed a milestone in Google’s evolution from search engine to walled-garden. In June of 2019, for the first time, a majority of all browser-based searches on Google resulted in zero-clicks. Read More
Google moves to prioritize original reporting in search
Nieman Labs’ Laura Hazard Owen provides some context on the most welcome change Google’s Richard Gingras announced last week. Of course there are questions around what ‘original reporting’ means, for Google and all of us, and we’ll have to see how well Google navigates this fuzziness. Read More
Designing multi-purpose content
The efficiency and effectiveness of multi-purpose content strategies are well known, as are many techniques for successful implementation. What is not so easy is justifying, assembling, and educating a multi-discipline content team. Content strategist Michael Andrews provides a clear explanation and example of the benefits of multi-purpose content designed by a cross-functional team that is accessible for non-specialists. Read More
Face recognition, bad people and bad data
Benedict Evans…
We worry about face recognition just as we worried about databases – we worry what happens if they contain bad data and we worry what bad people might do with them … we worry what happens if it [facial recognition] doesn’t work and we worry what happens if it does work.
This comparison turns out to be a familiar and fertile foundation for exploring what can go wrong and what we should do about it.
The article also serves as a subtle and still necessary reminder that face recognition and other machine learning applications are vastly more limited than what ‘AI’ conjures up for many. Read More
Also…
A few more links in this issue as we catch up from our August vacation.
The Gilbane Advisor curates content for content management, computing, and digital experience professionals. We focus on strategic technologies. We publish more or less twice a month except for August and December.