David Guenette has some cautionary thoughts for the publisher who–quite naturally–will be intrigued by Apple’s new services for publishers being brought to market by Jouve and Innodata-Isogen.
Category: Publishing & media (Page 21 of 54)
Vice President & Lead Analyst Ned May, our Outsell colleague, wrote an excellent Outsell Insights titled “Long Tail Publishers Now Have An Easy Route to Apple’s iBookstore.” The piece covers Apple’s selection of two conversion services for publishers to use to get book titles into the iBookstore. Here’s a key part:
Any publisher looking to get their books on the Apple platform now has an option to have their works converted to the appropriate format by one of two approved firms – Jouve and Innodata Isogen. Further, a publisher can initiate and complete the conversion in a relatively seamless fashion via the Apple iTunes Store site.
Whether these Apple-vetted companies will really offer a more rationalized conversion process than other such services remains to be seen, but May is right that in the controlled universe of the Apple platform, this sure won’t hurt.
What remains unlikely, at least for the present, is that book content conversion—even under such optimal arrangements—will prove as easy and inexpensive as a publisher might hope. Standards-based ebook formats—ePub, primarily—are not fully standard in the real world, in that various ereader platforms manifest the content in different ways. Not that this should be a surprise, given the history of technology standards being interpreted flexibly, not to mention the propensity of hardware makers to differentiate from other devices by other manufacturers by adding additional features or capabilities. Apple’s application of the ePub standard falls well within this tradition, although what differentiates the Apple approach from most other efforts is the monotheistic rigor applied: There is but one Apple, and thou shalt not have other platforms… well, you get the point.
And Apple works, it must be said. The iPad is a nice ereader (among other things), and the Apps store offers the means to sell content of sorts that ePub can’t really handle (as yet, but ePub 3.0 is coming, with enhancements, as it were). Publishers seeking salvation within Apple World are, with the addition of Jouve and Innodata Isogen to the priesthood, one step closer to the promised land. But the reality is that even standard-based ePub format work—the aforementioned Apple-targeted conversion offerings—is hardly going to be simple, easy, or push-button. The $20 dollar conversion fee per title presupposes an existing digital content file so clean and consistently formatted as to be virtually faith-based, but not scientifically likely. There are a lot of quality assurance efforts and other sorts of tweaking any publisher should be budgeting, even in paradise.
There remain many other important issues for book publishers to consider, starting with whether Apple World is enough. If not, then the Apple offer of easy iBookstore supply of iTunes-based ebook production simply helps ease only one part of a much larger market. Ned May astutely identifies Apple’s ebook conversion partners’ larger hopes, which is that publishers will seek wider ebook platform targets, and, therefore, turn to these same conversion services for help in implementing more basic digital workflow improvement, such as that based on an XML-Early model, which in turn helps the publisher output to a number of present ebook formats, not to mention being better prepared for new or updated and expanded ebook standard formats, across the larger range of ereader-specific display demands.
For Apple, making it easier for book publishers to pursue the Apple ebook devices makes sense, but book publishers need to think long term, and the Apple-controlled system of ebook production and sales is, at present, anyway, a nice short-term solution. Innodata and Jouve are thinking long-term, with their Apple-status providing a very good entrée for selling broader services to publishers.
But as apps and ebooks become more standardized through improvements in base-functionality of ePub and the settling out of ereader device differences, and distribution of both content files and associated marketing content become more rational, publishers may be attracted to more profitable sales channels, and find their Apple-centricity a barrier. Currently, agency models—touted by Apple, early on—leave 30% of the ebook price with the channel, and this sounds a lot better that traditional publishing wholesale rates that leave 50% of gross revenues on the table. It is true that current channels such as Amazon offer the very important value of supporting the discovery, sale, and download of a title, but as ebook formats and associated bibliographic content work is taken up by the publishers, the real service of existing ebook channels—iBookstore, Amazon, Google eBook, etc.—will become simply transactional (purchase) and file management (download of titles and presentation of bibliographic content) in nature. Such transactional and file management services will be highly automatic, and hence, low-cost to provide, and it is very likely that 30% going to such services will become far too much to pay, with either Amazon and the other currently dominant ebook sales channels competing on margin, or getting beat.
Sometime soon, as book publishers gain more control over their content workflows, use XML for multiple ebook format production, and better manage bibliographic and other channel-supporting metadata, even 30% margin going to online ebook retailers will be too much. There is an opportunity for content vending sites that gain sufficient revenue only from transactional fees, perhaps in the 5-10% range.
Apple is making iBookstore ebook and apps production easier for publishers, but sticking to the Apple way may make it harder for publishers to succeed more widely in the longer run.
Google eBooks made its awaited debut this past Monday, and the very next day Amazon presented its own related news. The upshot, basically, is that ebook formats are now more widely applicable across more devices, be they ereaders, smartphones, or PCs (the Web).
While the news is probably more important in terms of expanding publishing channels for ebooks, the trend is a positive one for book publishers struggling with ebook formatting issues. Unfortunately, in some ways, Google and Amazon’s newest announcements will further confuse the already confusing state of ebook formatting. See Ebook Formats are Starting to Make Sense… So be Prepared to Remain Confused during the Evolution, in the Gilbane Publishing Practice blog, for more.
Google Editions, now Google eBooks, has finally shown up, and as was widely anticipated, really will be an ebook game-changer. Technically speaking, Google eBooks is not revolutionary, but the promised transparency of ebook formats across a variety of reading environments (Sony and Barnes and Noble ereaders, desktops and notebooks, and various smartphone devices) is a comfort for both publishers and readers. There have been a number of other efforts—some, perhaps, more vapor than real—that promise much the same thing. Baker & Taylor’s Blio, for example, offers many similar benefits. PDF and ePub, too, claim a degree of trans-device applicability, and then there is the “apps” approach.
And now, again, there is Amazon. Right on the heels of Google’s announcement of Google eBooks, Amazon has followed the tried-and-true marketing playbook maneuver—also of value to yacht racing, I’m told—of taking the wind out of an opponent’s sails. By expanding Kindle for the Web, Amazon now “…enable[s] anyone with access to a web browser to buy and read full Kindle books—no download or installation required,” according to their December 7, 2010 press release. Amazon’s proprietary .AZW format, with its new, wider platform use, is combating the Google eBook promise of making ebooks easier to use “from the cloud.” Most likely, what Amazon is really trying to do is maintain its position relative to the marketplace’s desire to make ebook buying easier. Here’s Amazon’s positioning, from the aforementioned press release, on the matter:
“Kindle for the Web makes it possible for bookstores, authors, retailers, bloggers or other website owners to offer Kindle books on their websites and earn affiliate fees for doing so,” said Russ Grandinetti, Vice President, Kindle Content. “Anyone with access to a web browser can discover the seamless and consistent experience that comes with Kindle books. Kindle books can be read on the $139 third-generation Kindle device with new high-contrast Pearl e-Ink, on iPads, iPod touches, iPhones, Macs, PCs, BlackBerrys and Android-based devices. And now, anywhere you have a web browser. Your reading library, last page read, bookmarks, notes, and highlights are always available to you no matter where you bought your Kindle books or how you choose to read them.”
You could easily swap out Google for Amazon, plus one or two particular details, and be reading t from the Google press release from the day before. Google’s challenge will be to make buying ebooks as easy as Amazon, and neither the history of Google’s clunky interfaces generally, nor the first iteration of Google eBooks’ own web site specifically, convinces me that this will be a slam-dunk for Google.
Still, it is easy to see why publishers are happy with Google’s entry into ebooks, since it helps further shift selling options for ebooks away from the Amazon-centric model. As much as ebooks—especially for trade publishers—has happened in large part because Amazon got out in front and put real money up to make the market happen, more sales options, and less format-specific constraits for readers will help everyone.
You can rest assured that book publishers will continue to struggle to get ebook formats right for some time to come, despite the generous hype in these recent announcement. Kindle format limitations will still force publishers to balance quality and production costs, and ePub—heading for its 3.0 version sometime—will still hang up on the different features represented within different ereader devices capabilities.
That is just one reason why Outsell’s Gilbane Group’s Publishing Practice is developing a second study, following on the heels of A Blueprint for Book Publishing Transformation: Seven Essential Systems to Re-Invent Publishing. Ebooks, Apps, and Formats: The Practical Issues will looks at the topic of content format, because this remains a central concern for book publishers pursuing digital publishing programs, and involves a wide-ranging set of issues from editorial and production to distribution and ecommerce.
With Google eBooks and Amazon’s for the Web, ebook formats and their marketplace continue to evolve. It sure ain’t “push-button” yet, however.
Stay tuned. Drop a note.
Bill Trippe and I were speaking with someone at a mid-sized education publisher the other day, and we heard a well-informed and articulated series of complaints about the Kindle format. The frustration behind these comments was palpable: Kindle is where so much of the early and encouraging growth of the ebook market has happened, but the E-ink display and .AWZ format is really not good for any content beyond straight-forward text constrained within narrative paragraph structure. While such constraint works fine for many titles, any publisher producing educational, professional, STM, or any other even moderately complex content has to compromise way too much.
Book publishers still not committing to the ebook market certainly like the news of the potential—Forrester’s James McQuivey, with the projection of the ebook market hitting $3 billion in sales sometime soon, is the latest word, perhaps—but these same book publishers, who after all, are the ones having to do the work, find themselves wondering if they can get there from here. Hannah Johnson, at PublishingPerspectives, posted a blog titled “Forrester’s James McQuivey Says Digital Publishing is About Economics, Not Format” The post is on the post by James McQuivey of Forrester Research about the projected growth of ebook sales and the emphasis on economics, not formats, when assessing ebooks’ future.
McQuivey’s point is right, of course, although it isn’t a startling conclusion, but one more on par with pointing out that, for print books, it matters very little whether the title comes out in hard cover or paperback, or in one trim size over another. Still, in today’s ebook hysteria, it remains valuable to point out the sensible perspective.
In book publishing, the main consideration is producing a book that is of strong interest to readers, while also making sure that these readers can get their hands on the title in ways that produce sufficient monetary gain for the publisher. The only reasons why ebook formats are such a concern at the moment is that the question of ebook formats is a new one that book publishers are struggling to figure out how to implement, even while the marketplace for any and all such ebook formats remains nascent.
The Gilbane Group has been in the business of helping companies with all kinds of content—including publishers of many stripes—more effectively manage their content and get it to those who need it, at the right time, in the right form. Our recent 277-page study, A Blueprint for Book Publishing Transformation: Seven Essential Systems to Re-Invent Publishing (which is free, for download, by the way), discusses the issue of ebook formats and makes the point that book publishers need to move toward digital workflow—and, preferably, XML-based—as early in the editorial and production process as possible, so that all desirable formats the publisher may want to produce now and in the years ahead can be realized much more efficiently and much less expensively. One section in our industry forecast chapter is titled, “Ebook Reader Devices in Flux, But so What?”
But good strategic planning in book publishing doesn’t necessarily resolve each and every particular requirement for market success, and given the confused state of ebook format s and their varying production demands, we’re developing our next study that drills down on this very issue. Working title: Ebooks, Apps, and Formats: The Practical Issues.
Stay tuned. Drop a line.
As absurd as the title of this entry sounds, there is a point to it, especially when you consider all the theories being bandied about the consequences of book publishing’s encounter with ebooks specifically, and digital publishing generally. The sheer range in such theories is impressive, from the “print is dead” silliness (unless, perhaps, you are casting well into the future) to much more reasonable suppositions that book publishers as they are today may be in danger of disintermediation tomorrow (or, rather, 5, 10, or more years down the road), as digital technologies may engender significant shifts in the supply and value chains presently in place. There’s plenty of compelling evidence that real alternatives will exist, and are found in our newest study on book publishing and ebooks, A Blueprint for Book Publishing Transformation: Seven Essential Processes to Re-invent Publishing, now available for free download. One such statistic is from Bowker’s own analysis of the book industry, where it reports the number of new fiction titles being traditionally published dropped significantly from 2008 to 2009, while the overall number of book titles published, including fiction, exploded due to non-traditional publishing efforts such as “self-publishing” and ebooks.
Don’t write off book publishers yet, however. We see that book publishing across all segments—from trade, to educational, STM, and professional—have been making good progress, especially in approaching digital workflow as a necessary process improvement, and, even with the use of XML for content creation and management within such workflows. While the industry as a whole still can’t be thought of as all that fast moving (after all, many book publishers still take a year or two to get a signed book into the hands of readers), speculation that these “dinosaurs” are doomed is simply unsupportable.
Blueprint provides an in-depth look at publisher responses to digital mandates, identifies winning strategies for ebook technologies, processes, and systems. One of the sponsors of this multi-sponsor study is the Book Industry Study Group (BISG), and in a letter to its members about the recently published Blueprint, BISG’s Executive Director, Scott Lubeck writes:
We all hear a great deal about change in our industry, but very little on how to accomplish this in a constructive way. The key to managing change is not mastering technology—however important that may seem to be—but rather in mastering process. If you don’t understand the processes that underlie and drive your businesses you can’t change them let alone improve them, you can only watch them collide, and in the worst cases implode, as new opportunities emerge or new competencies are required.
It is the very fact that book publishing entails many processes which places the industry in the captain’s chair, even as self-publishing has its role to play as more and more services are available to self-publishers that reflect the wide range of processes (e.g., think promotion and marketing, for one) involved in book publishing. Book publishers know their business processes, and there is little that is simple about most publishing processes. Lubeck writes of one element of publishing that key to improving many publishing processes:
Good process and process awareness produce enormous value in the book industry value chain. The most salient example to my mind is metadata. Metadata is not one thing: there are bibliographic metadata, production metadata, marketing metadata, product metadata, just for starters; and all metadata maps to the core publishing process that produce it. If you want to improve metadata—and you better had in order to succeed in the digital world—you have to understand and improve these processes. The technologies follow.
Now, I’m not going to suggest that book publishing as a whole—and more so in some segments than others—has no significant challenges. Book publishing carries, in many of the companies, high debt loads, and the overall margins can be modest. And long-established industries—think music recording—can all too easily be their own worst enemies, refusing to respond to changing market realities, and there’s no guarantee that book publishing won’t be equally stupid.
But it looks good so far, perhaps because publishing has long been struggling with debt and margins and has been desperate for reducing costs and increasing revenue. Digital technologies, when applied in service to publishing processes that are sound, serve these ends quite effectively.
Let us know what you think. Leave a comment. Drop a line.
If you have been following recent XML Technologies blog entries, you will notice we have been talking a lot lately about XML Smart Content, what it is and the benefits it can bring to an organization. These include flexible, dynamic assembly for delivery to different audiences, search optimization to improve customer experience, and improvements for distributed collaboration. Great targets to aim for, but you may ask are we ready to pursue these opportunities? It might help to better understand the technology landscape involved in creating and delivering smart content.
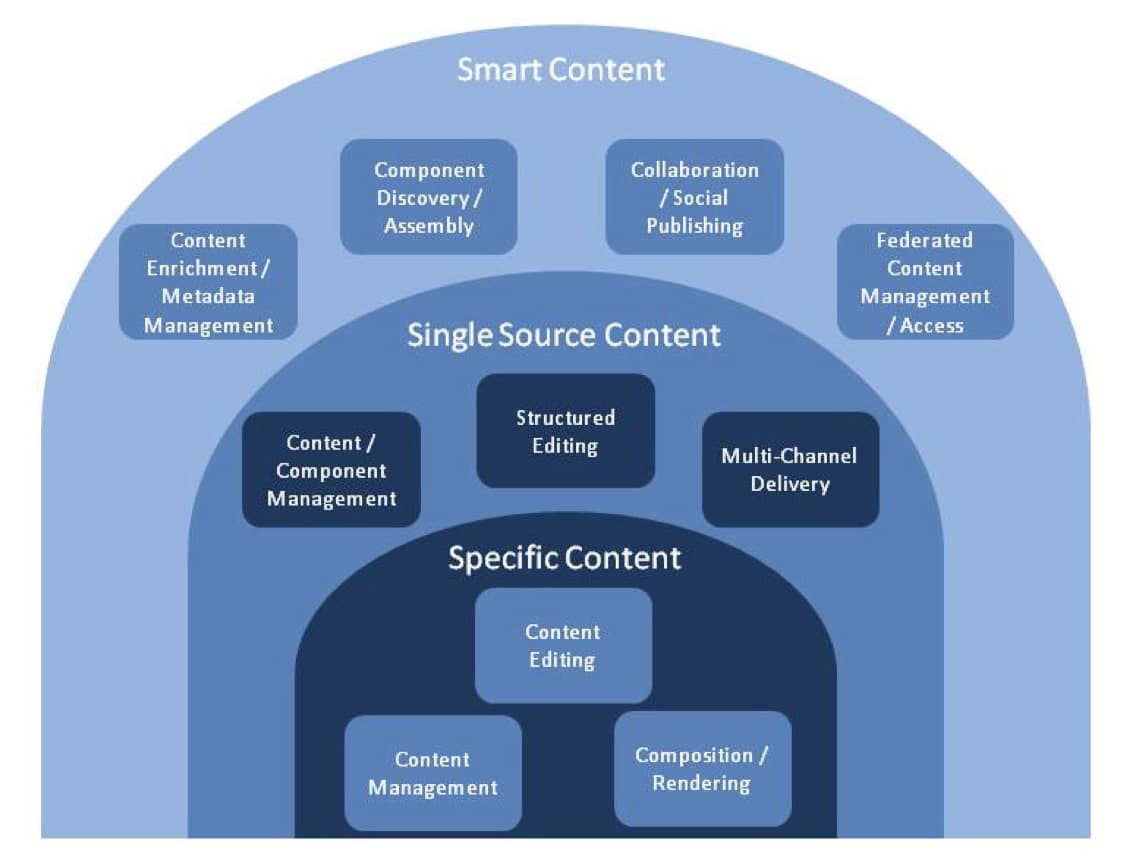
The figure below illustrates the content technology landscape for smart content. At the center are fundamental XML technologies for creating modular content, managing it as discrete chunks (with or without a formal content management system), and publishing it in an organized fashion. These are the basic technologies for “one source, one output” applications, sometimes referred to as Single Source Publishing (SSP) systems.
The innermost ring contains capabilities that are needed even when using a dedicated word processor or layout tool, including editing, rendering, and some limited content storage capabilities. In the middle ring are the technologies that enable single-sourcing content components for reuse in multiple outputs. They include a more robust content management environment, often with workflow management tools, as well as multi-channel formatting and delivery capabilities and structured editing tools. The outermost ring includes the technologies for smart content applications, which are described below in more detail.
It is good to note that smart content solutions rely on structured editing, component management, and multi-channel delivery as foundational capabilities, augmented with content enrichment, topic component assembly, and social publishing capabilities across a distributed network. Descriptions of the additional capabilities needed for smart content applications follow.
Content Enrichment / Metadata Management: Once a descriptive metadata taxonomy is created or adopted, its use for content enrichment will depend on tools for analyzing and/or applying the metadata. These can be manual dialogs, automated scripts and crawlers, or a combination of approaches. Automated scripts can be created to interrogate the content to determine what it is about and to extract key information for use as metadata. Automated tools are efficient and scalable, but generally do not apply metadata with the same accuracy as manual processes. Manual processes, while ensuring better enrichment, are labor intensive and not scalable for large volumes of content. A combination of manual and automated processes and tools is the most likely approach in a smart content environment. Taxonomies may be extensible over time and can require administrative tools for editorial control and term management.
Component Discovery / Assembly: Once data has been enriched, tools for searching and selecting content based on the enrichment criteria will enable more precise discovery and access. Search mechanisms can use metadata to improve search results compared to full text searching. Information architects and organizers of content can use smart searching to discover what content exists, and what still needs to be developed to proactively manage and curate the content. These same discovery and searching capabilities can be used to automatically create delivery maps and dynamically assemble content organized using them.
Distributed Collaboration / Social Publishing: Componentized information lends itself to a more granular update and maintenance process, enabling several users to simultaneously access topics that may appear in a single deliverable form to reduce schedules. Subject matter experts, both remote and local, may be included in review and content creation processes at key steps. Users of the information may want to “self-organize” the content of greatest interest to them, and even augment or comment upon specific topics. A distributed social publishing capability will enable a broader range of contributors to participate in the creation, review and updating of content in new ways.
Federated Content Management / Access: Smart content solutions can integrate content without duplicating it in multiple places, rather accessing it across the network in the original storage repository. This federated content approach requires the repositories to have integration capabilities to access content stored in other systems, platforms, and environments. A federated system architecture will rely on interoperability standards (such as CMIS), system agnostic expressions of data models (such as XML Schemas), and a robust network infrastructure (such as the Internet).
These capabilities address a broader range of business activity and, therefore, fulfill more business requirements than single-source content solutions. Assessing your ability to implement these capabilities is essential in evaluating your organizations readiness for a smart content solution.
Our Blueprint study is the first in-depth look into ebook-related issues from the book publishers’ perspective, tying digital considerations to the everyday book publishing processes (A Blueprint for Book Publishing Transformation: Seven Essential Processes to Re-Invent Publishing.) Book publishers across all segments are embracing ebooks, but they require guidance grounded in what they actually do, more than simply a focus on technology.
See my blog in Publishing Practices about some of our Blueprint findings.
And let us know what you think!